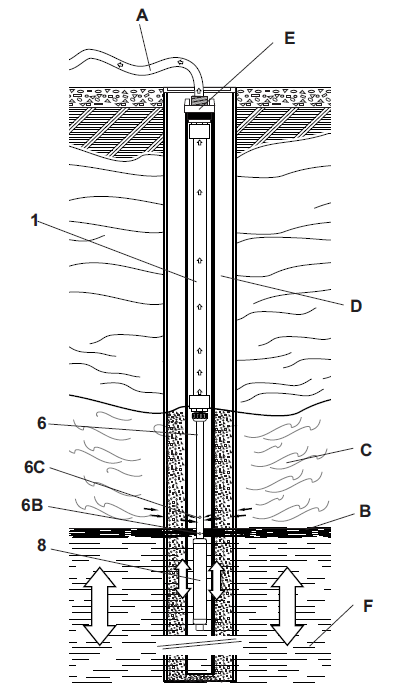
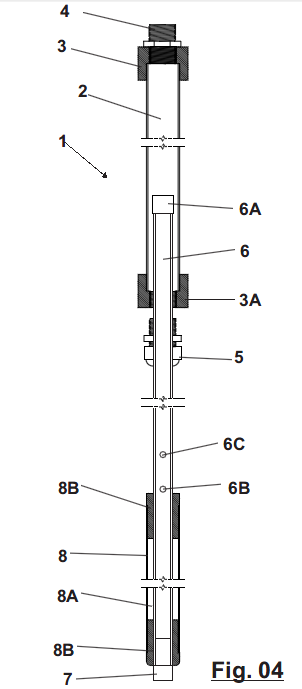
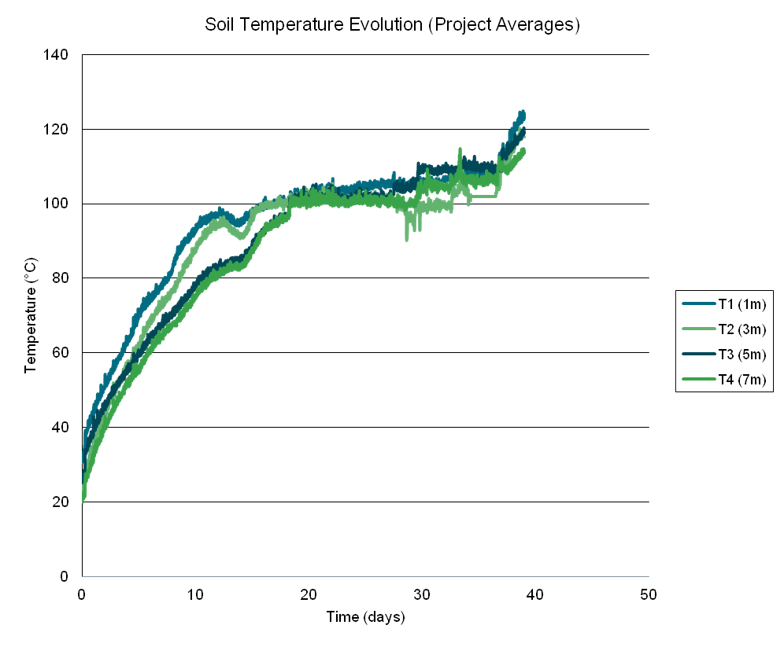
Environmental Remediation
Environmental remediation techniques exist to preserve natural resources and human health. Technological evolution has provided various remediation techniques for soil and water. Each technique, however, has its limitations and specificities. Among the main techniques adopted worldwide, GEOAMBIENTE works with the following:
Pumping & Treatment
P&T is an emergency technique, used when it is desired to remove large volumes of free phase contamination or avoid advancement of a certain contamination, through the creation of a hydrogeological barrier. The process basically works by pumping and drawdown groundwater at the affected area.
Multiphase Extraction
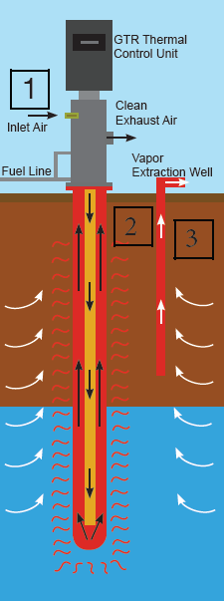
Soil Vapor Extraction
This technique is also applied to volatile compounds or with high volatilization. Typically used in soil where contamination has not reached or has no shallow groundwater, and it can also be applied in conjunction with other remediation techniques.
Air Sparging
It is based on pressurized air injection into the groundwater, aiming to support the stripping process of volatile substances dissolved in the water and its resulting remediation. Air sparging process may be linked to SVE / MPE processes. Its applicability should be rigorously evaluated in several respects, especially if there is neighborhood where it is wanted to remedy, because its use generates volatile substances in the atmospheric environment and can aid to spread contamination in the groundwater.
Natural Attenuation
Natural attenuation process involves monitoring procedures of physical, chemical, nutritional and microbiological parameters of local soil and aquifer, together with application of nutrients and dissolved oxygen in form of peroxide, or other promoters of oxygen emission, in order to assist the process of biodegradation of remaining organic compounds.
Oxidants Injection
The oxidizing agents most commonly used are Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2), Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4), Magnesium Oxide (MgO2), among others. The compounds release oxygen in the groundwater aquifer, aiding in oxidation processes, wherein hydrocarbons are converted to CO2 and H2O. Its use also requires some care, since the compounds are highly reactive and can cause structural damage to the subsoil, because they may react violently.
Surfactants
Using surfactants has its applicability when contaminants are strongly bonded in the soil matrix, avoiding their release by traditional means. Thus, it is specifically applied according to the contaminant, and can be used surfactants which release the contaminant to the aqueous media, allowing its capture by traditional methods. Surfactants should also be used with great technical criterion, because contamination´s spread may free a problem trapped so far.